Ethernet cable wiring guide
Discover the essentials of Ethernet cable wiring in this informative guide by Electronic Team. Whether you're a networking novice or a seasoned professional, this article covers everything from cable types and categories to wiring standards like T568A and T568B. Learn how to wire Ethernet cables step by step, understand RJ45 connectors, and explore which cable is best suited for your network setup. Perfect for anyone looking to optimize their wired connections!
Table of contents:
- General information about Ethernet cable
- What are the types of Ethernet cables?
- Ethernet cable wiring
- Ethernet cable connector types
- Ethernet RJ45 connection wiring and cable pinout
- How to wire Ethernet Cables [Step-by-step guide plus Video instruction]
General information about Ethernet cable
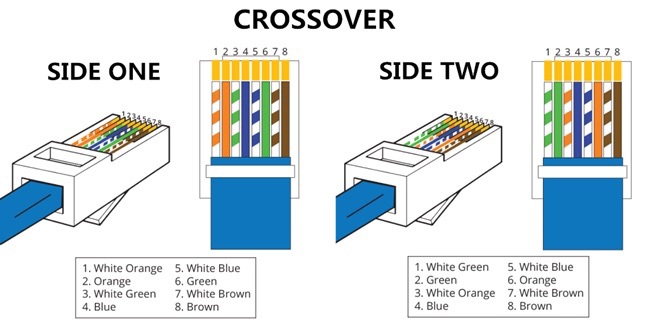
Connecting a computer to a network such as the Internet can be accomplished either with a WiFi or a wired connection. Long before WiFi was available Ethernet cables were the only option to attach a machine to a network. Ethernet cables are primarily connected to a computer at one end and a network switch or router on the other end. Crossover cables are specialized Ethernet cables that are used to directly connect two computers to each other.
Without Ethernet cables, the World Wide Web and the Internet as we know it could not exist. Those inventions, which have become indispensable in the modern age, would have been impossible without the network connectivity made possible by Ethernet cables.
There are two main categories of Ethernet cables - braided stranded cables and solid cables. The solid cables are more useful for use in fixed locations with the stranded cables better at flexible desktop use.

What are the types of Ethernet cables?
There are 5 different types of Ethernet cables available on the market today. They are Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, and Cat7. The most commonly used cables are of type Cat5 and Cat5e.
Let’s take a closer look at what distinguishes the different kinds of Ethernet cables.
Cat5 - Standing for Category 5, the Cat5 follows its predecessors Cat3 and Cat4 cables. It is the most used type of cable and until the arrival of Cat5e was considered the most efficient and reliable option available. It is made of unshielded twisted pairs (UTP) of wires and has maximum data transmission speeds of 10/100 Mbps.
Cat5e - This is an enhanced version of the Cat5 cable that offers better speed and protection from electrical interference. It is also a UTP cable and can reach transmission speeds of 1000 Mbps.
Cat6 - Category 6 cables increase the transmission performance of the Cat5e variety. Both kinds can handle Gigabit speeds, but Cat6 is better suited to environments where more electromagnetic interference may be present. Cat6 cable is available in both UTP and STP (shielded twisted pairs) form and is more expensive than Cat5e. Its top speed is 1000Mbps.
Cat6a - Augmented Category 6 cable increases transmission speed to 10,000 Mbps and doubles the maximum bandwidth to 500 MHz.
Cat7 - Category 7, also known as Class F cables are comprised of screened, shielded twisted pairs (SSTP) of wires. They are more heavily insulated and are thicker and bulkier that Cat6e cables. They are hard to bend but achieve data transfer speeds of 10,000 Mbps over bandwidths of 600 MHz.
Different Ethernet Categories
| Cable Type | UTP | UTP | UTP or STP | STP | S/FTP |
| Max. Data Transmission Speed |
10/ 100/ 1000 Mbps | 10/ 100/ 1000 Mbps | 10/ 100/ 1000 Mbps | 10,000 Mbps | 10,000 Mbps |
| Max. Bandwidth | 100 MHz | 100 MHz | 250 MHz | 500 MHz | 600 MHz |
Ethernet cable wiring
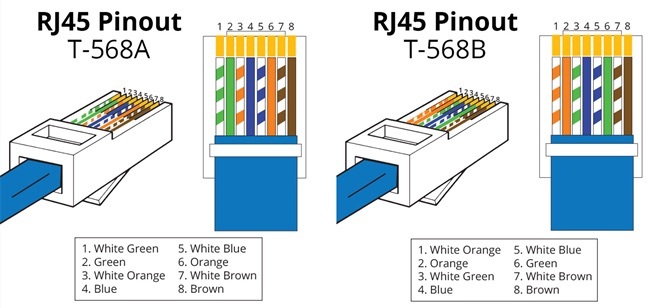
There are four twisted pairs of wires inside every Ethernet cable. An ethernet cable wiring diagram will show that only two of these pairs are actively used in the transmission of data. The Orange and Green pairs of wires are used in both the T568A and T568B standards, but for different purposes.
In the T568A standard, the Orange and White/Orange pair of wires is used to receive data with the Green and White/Green pairs used to transmit. In addition to having the wires in a different pinout configuration, the T568B style cable reverses the transmission and receiving pairs. It transmits through the Orange wires and receives data through the Green pair.

Ethernet cables are wired in a specific way and the internal wires conform to an Ethernet cable color code. There are 8 wires inside an Ethernet cable. They are twisted into four pairs of wires that follow the color code for Ethernet cables. A pair will consist of a solidly colored cable and a white cable with a stripe of the solid color. In some cases, there is no stripe so the only way to tell which white wire you are handling is to determine the color of the solid wire in the pair.