VirtualBox Webcam Passthrough: Using A Host Webcam On A Guest Machine
When you need USB passthrough in VirtualBox, you may first look for native solutions. While third-party software can simplify the process, Oracle VM VirtualBox includes built-in support that can be configured manually.
VirtualBox offers a feature called “Webcam Passthrough,” which allows a guest system to access and use the host machine’s webcam. This feature complements the general USB passthrough support, which was the primary method for accessing webcams in earlier versions of VirtualBox.
Contents:
Using VirtualBox Webcam Passthrough
The webcam passthrough feature in VirtualBox can theoretically handle non-USB video sources. However, this capability is currently untested, and results may vary depending on hardware and host configuration. This information is based on Oracle’s documentation.
To implement additional settings in VirtualBox, you will need to install the VirtualBox Extension Pack.
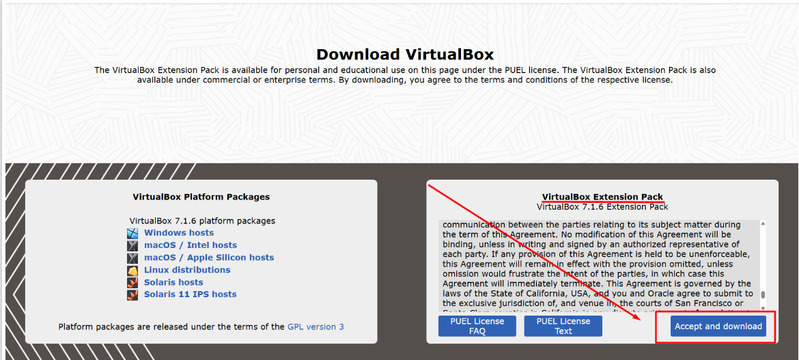
Here is the view of the extensions right now.
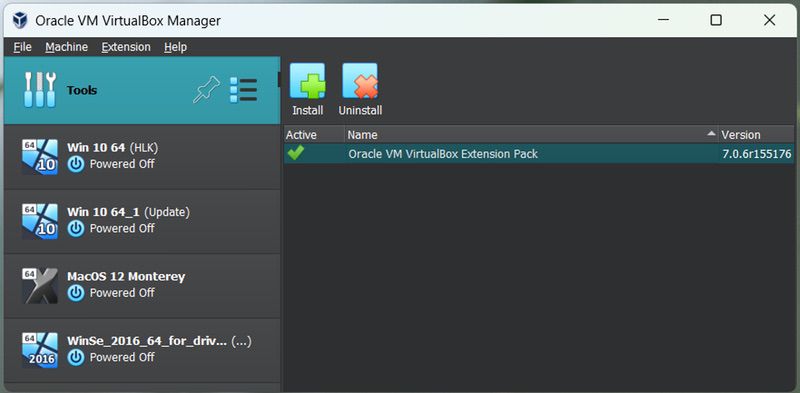
Please Note: Webcam Passthrough modules come standard with Oracle VM VirtualBox Extension Packs, but Extension Packs will need to be installed separately.
Host webcams can be connected to VMs through: VM Menu Bar> Devices Menu. Users will find a list of available (host) video input devices in the webcam menu. When a user clicks the webcam name, it connects or disconnects the relevant host device.
To enable webcam passthrough, use the VBoxManage command line tool. See host-specific sections outlined below for more information.
Below is a list of available commands:
List of host webcams and video input devices
$ VBoxManage list webcams
See output format below:
Alias= "User-Friendly Name"
Host Path or Identifier
An alias is used to shortcut within other commands. The ‘.0’ alias describes the host default video input device. ‘.1’ and ‘.2’ describe the first and second (and so on and so forth) video devices. Device order is unique to each host machine.
Connect A Webcam To A Running VM Session:
Run the command:
VBoxManage controlvm VM name webcam attach [host_path|alias [settings]]
The USB webcam will now attach to the guest computer
The following shows that setting parameters are strings: “Setting1=Value1”, ”Setting2=Value2”, etc... The setting parameters allow users to configure the webcam device being emulated.
See the supported settings below:
MaxFramerate: The highest frame rate that can be sent to the guest machine. High frame rates need increased CPU power, so it’s beneficial to set lower frame rate limits.
Default = “no limit”, allowing the guest to access and utilize any and all frame rates that the host webcam can support.
MaxPayloadTransferSize: The maximum amount of bytes that the emulated webcam can transfer to the guest machine at one time.The default value used by numerous webcams is “3060”.
If the guest machine can utilize larger buffers, higher byte value can (minorly) reduce the load on a CPU. The only issue that may arise is whether a high MaxPayloadTransferSize is supported by the guest machine in use.
How to detach A Webcam From A Running VM Session:
“VBoxManage controlvm VM-name webcam detach [host_path|alias]”
List the webcams connected to an active VM as shown below:
“VBoxManage controlvm VM-name webcam list”
Per each attached webcam: the output contains the alias or path in use by the “webcam attach” command.
VirtualBox Webcam Passthrough: Windows Hosts
Emulated webcam devices automatically disconnect from guest machines when webcams are detached from host machines.
VirtualBox Webcam Passthrough: Mac OS X Hosts
Only versions of Mac OS X 10.9 or newer are compatible with VirtualBox Webcam Passthrough.
Emulated webcam devices remain connected to guest machines, even when webcams are disconnected from host machines. This means that users must manually disconnect by using the: “VBoxManage controlvm VM name webcam detach” command.
VirtualBox Webcam Passthrough: Linux and Oracle Solaris Hosts
Once the webcam is disconnected from the host, the device emulation on the guest machine automatically disconnects only if the webcam is streaming video.
If the webcam being emulated isn’t active, manual disconnection is necessary using the: “VBoxManage controlvm VM name webcam detach” command.
Aliases: ‘.0’ and ‘.1’ are both mapped to “/dev/video0”.
Alias ‘.2’ maps to “/dev/video1”